A Computer-Based Exercise on the Racemization Mechanism and Energy Barrier of Axially Chiral Molecules
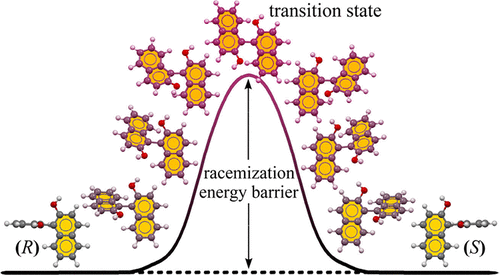
Chirality is a fundamental property of nature, but it is challenging for undergraduate students to anticipate and understand the mechanism of racemization. In the density-functional-theory-based exercise described herein, students are introduced to tasks ranging from simple to complex to search transition states in the racemization process of a series of axially chiral biaryl molecules. The calculated racemization energy barriers range from 16.7 to 54.3 kcal/mol, mainly depending on the degree of steric hindrance between four ortho-position substituents. This visual and straightforward exercise is designed to stimulate students’ interest in organic and physical chemistry, provide insight into chemical mechanisms, and reveal the intrinsic relationships between structure and property.
Reference
Zijun Guan, Li−Li Liao, Yong-Yuan Gui, Cefei Zhang, Xiangge Zhou, Da-Gang Yu, Haifeng Xiang, J. Chem. Educ., 2025, doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.5c00265